The sum of all stages of a parasite's ontogeny and its route of transmission from one host to another is called its life cycle.
loop form
The whipworm developmental cycle does not require an intermediate host.
Characteristics of cycle stages
The intermediate and final vectors of the parasite depend on the type of helminthiasis.
- Dispersal – This cycle exists when an intermediate host (i. e. source rather than final stage) is considered to be the only option at the moment (i. e. no potential final host exists). In this case, an intermediate host is used for further development and nutrition.
- Active Growth - After reaching the most suitable conditions, the parasite will stop, repair itself if suitable equipment is available, and begin growing to sexual maturity.
- Migration to another habitat – After mature individuals lay eggs, they in most cases move to further develop. They can be distributed in different ways. Most commonly, parasites migrate through the digestive system along with food boluses. Others, due to their size, can easily penetrate the bloodstream and spread throughout the body.
- Asexual Reproduction – A characteristic of certain types of parasites is that they do not require a second partner to reproduce. The most striking example is the tapeworm, in which each coccidia has a uterus in which mature eggs can be produced.
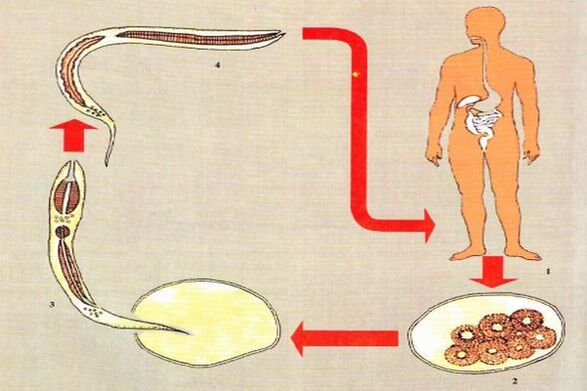
important concepts
Parasite development begins when the parasite enters its final host.
The concepts of "parasite reservoir" or "reservoir host" are also distinguished. This is a host in which pathogens can survive for long periods of time, accumulate, multiply, and spread to surrounding areas.
parasite biology
- Mechanical;
- poisonous;
- food withdrawal;
- Destroy tissue integrity.
- Humanization – humans serve as hosts;
- Zoonoses – multiple animals serve as reservoirs;
- Zoonotic diseases are common invasive infectious diseases in humans and animals.
- Protozoan parasites - Protozoology.
- Parasites, helminths - Helminthology.
- Arthropods - Arachnology.
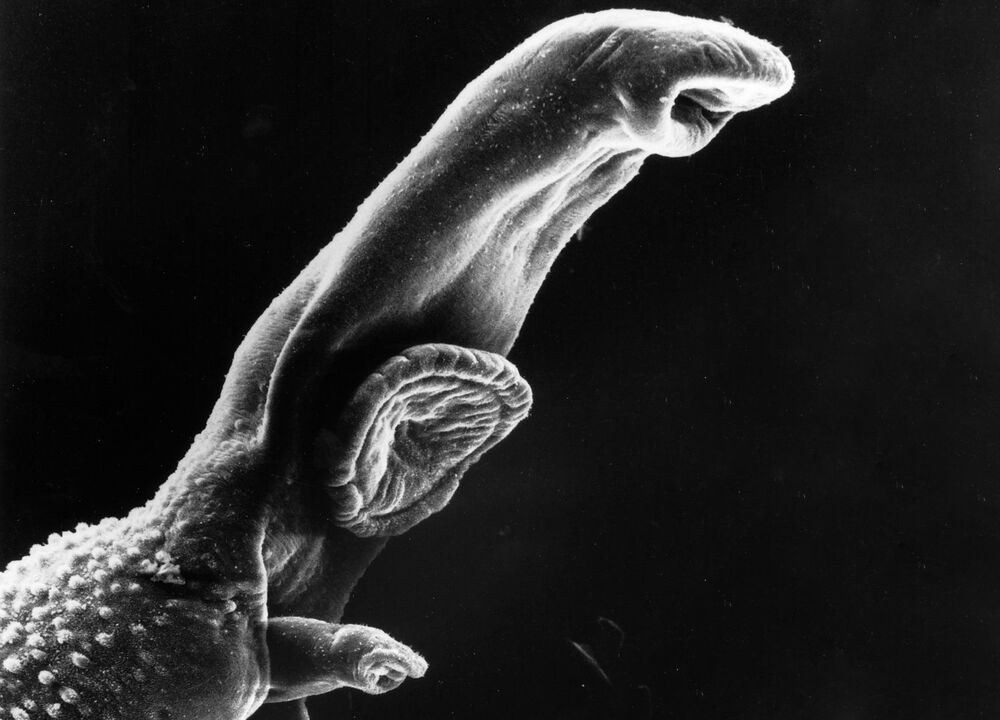
life cycle stage
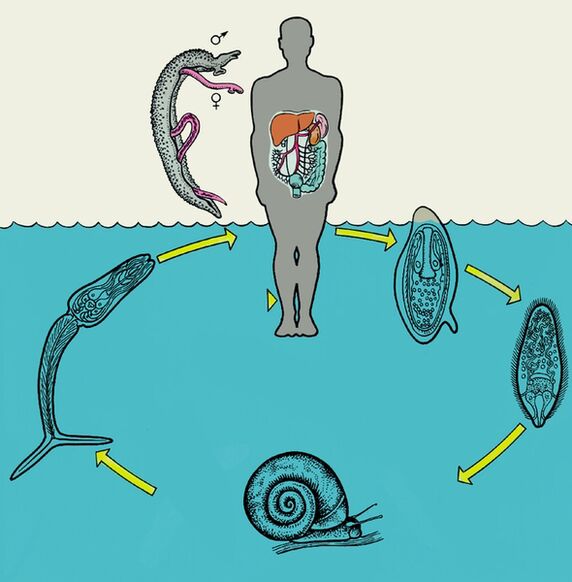
The invasive stage of the malaria parasite is the sporozoite.
Worm group
biological worm
Biological worms include most representatives of flatworm types.






































